LYMPHEDEMA
What is lymphedema?
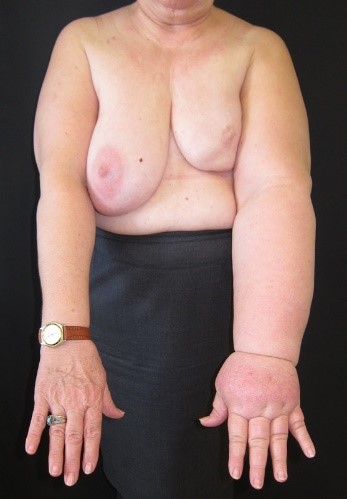
Lymphedema is a swelling of a part of the body, usually a limb, due to the absence or dysfunction of the lymph nodes or lymphatic vessels. It can be primary (congenital) or secondary (acquired). Secondary lymphedema cases can occur more often than primary, and usually starts several months or even years after a surgical procedure of axillary, inguinal or neck lymph node resection with or without additional radiotherapy.
|
|
|
Photos of patients with left upper limb and left lower limb lymphedema
According to the International Society of Lymphology, stages of lymphedema are:
Stage 0 – latent or subclinical condition where swelling is not yet evident despite impaired lymph transport, subtle alterations in tissue fluid/composition, and changes in subjective symptoms.
Stage I – represents an early accumulation of fluid relatively high in protein content (e.g., in comparison with "venous" edema) which subsides with limb elevation. Pitting may occur.
Stage II – involves more changes in solid structures, limb elevation alone rarely reduces tissue swelling, and pitting is manifest. Later in Stage II, the limb may not pit as excess subcutaneous fat and fibrosis develop.
Stage III – lymphostatic elephantiasis, where pitting can be absent and trophic skin changes such as acanthosis, alterations in skin character and thickness, further deposition of fat and fibrosis, and warty overgrowths have developed.
Ποιες είναι οι διαγνωστικές εξετάσεις;
Which are the diagnostic examinations?
Lymphoscintigraphy
Lymphoscintigraphy is performed in nuclear medicine laboratories. It provides information regarding the existence or absence of functioning lymph nodes, and the amount of the lymph fluid that is extravasated creating the dermal back flow of the upper or lower limb.
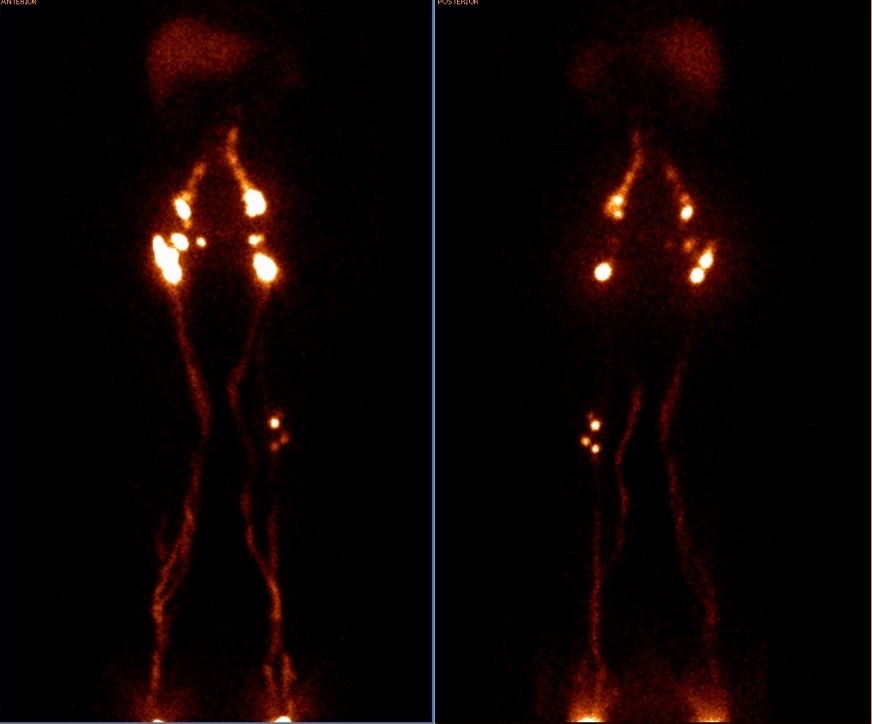
Photos of lower limb Lymphoscintigraphy (anterior and posterior view)
Superficial Lymphangiography
Superficial lymphangiography with direct fluoroscopy after the injection of indocyanine green represents the 'gold standard" method for documenting and recording lymphedema. It provides information regarding lymph circulation in the superficial lymphatic network and in the lymph vessels which are located at a depth of 0.5 – 2 cm from the skin, the number and shape of the lymphatic vessels, the site of the affected lymph nodes and the accumulation of lymph, while finally determines the severity stage of lymphedema.
The International Society of Lymphology has adopted the Yamamoto's dermal back flow staging to characterize the morphology of the lymphatics as:
a) Linear (Lymphedema Grade A)
b) Splash (Lymphedema Grade B)
c) Stardust (Lymphedema Grade C)
d) Diffuse (Lymphedema Grade D)
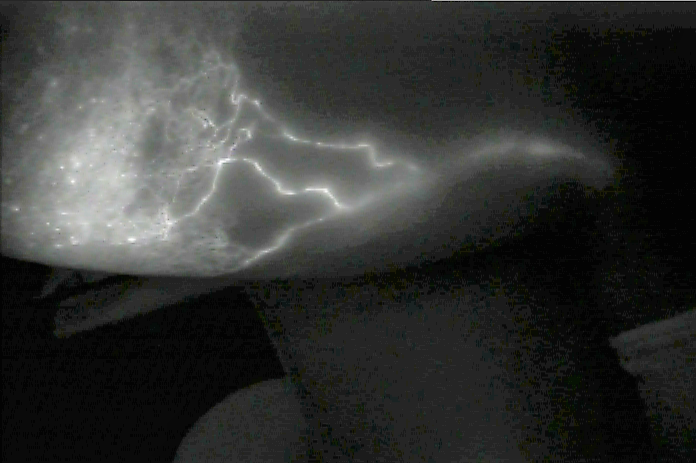
Picture of superficial ICG lymphangiography of an upper limb lymphedema
SPECT/CT
The evolution of lymphoscintigraphy for diagnosing lymphedema is the hybrid nuclear medicine examination named SPECT-CT lymphangiography. It is an amalgamation of a lymphoscintigraphy and a CT at the same gantry. It provides functional information of lymph nodes and lymph flow in an anatomical location.

Picture of pelvic limb SPECT/CT to select the appropriate lymph node flap for a lymphatic microsurgery procedure
MRL
Magnetic Resonance Lymphangiography (MRL) is a special magnetic resonance imaging that depicts the quality of the lymph vessels and lymph nodes of the deep space, the accumulation of lymph in the subcutaneous tissues, and the severity of lymphedema. The examination is carried out in specialized radiology laboratories.
What are the treatments options for lymphedema?
Conservative
Manual Lymphatic Drainage
Manual Lymphatic Drainage (MLD) is a specialized type of light rhythmic movements to stimulate the lymphatic system and guide the lymph out of the affected limb. After completion of each session, a special "wrapping" of the limb with specific elastic bandages, helps the limb to reduce the swelling. An elastic custom-made garment (sleeve or stocking) is finally recommended to control the limb volume and avoid lymphedema recurrence.
Pump therapy
Utilization of intermittent pneumatic compression pumps is a simple and easy solution for management of lymphedema of the upper and lower extremities, when a MLD is difficult to be performed. Their use can be exploited both for the preparation of the limb for the surgical treatment, and for the postoperative rehabilitation.
Compression elastic garments
The management of any chronic oedema is always completed with the application of the appropriate compression elastic garment. A necessary condition before its use is the reduction of the swelling with comprehensive decongestive treatment. Elasticity of the garments usually lasts for six months before their replacement.
Skin care
The burdened lymphatic circulation and affected defenses of the lymphedematous limb sometimes create chronic skin ulcers, especially in the lower extremities. Chronic ulcers in patients with lymphedema are often due to a combination of diseases, e.g. lymphatic stasis and venous insufficiency or diabetes mellitus, etc.
Prevention is the best way to deal with chronic ulcers. This is achieved through: regular cleaning of the skin, which prevents the occurrence of local infections, use of moisturizer offers good firmness to the skin and protects against easy injuries and scratches, and regular dressing changes of ulcers which allows healing.
Diet & Exercises
Proper and balanced nutrition plays important role in supporting the treatment of lymphedema. The goal is to lose weight and maintain healthy way of living.
Exercising before and/or after lymphedema surgery eases the recovery period. With the necessary training program, which includes aerobic exercise, Yoga, Pilates, and stretching, faster recovery and reduction of the volume of the affected limb are achieved.
It is generally recommended for all lymphedema patients.
Surgical treatment
Vascularized Lymph Node Transfer
Vascularized lymph node transfer is a physiological functional method of treating lymphedema. The aim of the operation is to transfer 2-3 functional lymph nodes from a healthy area of the body to the limb suffering from lymphedema. The vessels of the transferred lymph nodes are connected, to the vessels of the affected area, with the use of surgical microscope. Lymphangiogenesis starts immediately and restores gradually the lymphatic circulation.
|
|
|
Schemes of lymph node flap transferred in axilla and calf.
Lymphaticovenous anastomosis (LVA)
Lymphaticovenous anastomosis (LVA) describes the microsurgical connection of lymphatic vessels to the small veins nearby and constitutes, the "bypass" of lymph from the lymphatic vessels to the blood vessels. LVAs are performed under general or local anesthesia at the points selected and noted after superficial lymphangiography.
LVAs are usually applied to patients who are in the early stages of lymphedema or in combination with lymph node transfer, for faster reduction of the volume of the affected limb.
Lipectomy / Liposuction
After surgical treatment of lymphedema with lymph node transfer or lymphaticovenous anastomoses, lymphedema often turns into lipedema. The technique which is used to treat the excess adipose tissue (fat) component is liposuction. It removes the adipose tissue of the body through small halls. Postoperative care must be taken with application of elastic garments for a significant period according to the severity of the disease.
Lipectomy is also applied in cases that LNT or LVA is not recommended.
Skin and adipose tissue resection - Dermolipectomy
Large volume lymphedema or elephantiasis can be benefit from surgical excision of skin and adipose tissue of the same area. The operation has the advantage of immediate removal of large excess tissue volume, while it is a procedure with serious risks and long recovery time
LIPEDEMA
What is lipedema?
Lipedema is a condition of the subcutaneous adipose tissue, which appears as swelling of bilateral extremities (mainly lower and occasionally upper) with fat accumulation. It affects almost 1 in 10 women and appears to have a hereditary predisposition.
Symptoms include severe pain mainly at the lower leg, feeling of heavy legs which deteriorates during standing, intolerance to pressure or sometimes simple skin contact, easy bruising and often appearance of varicose veins.
It usually starts during puberty or other periods of hormonal disorders. Weight gain worsens the presence of lipedema, but weight loss does not guarantee volume reduction in swollen limbs. Despite exhausting diets or increased exercise, people with lipedema do not see significant improvement.
It is often mistakenly be confused with lymphedema or lipodystrophy, while differential diagnosis is mainly made through meticulous clinical examination.

What are the treatments options for lymphedema?
Lipedema can be treated surgically with a procedure that aims to reduce the excess adipose tissue (fat) of the affected area.
Lipectomy (Liposuction)
The surgical procedure of lipectomy is used to treat lipedema with the use of liposuction technique. It removes the excess fat of the body through small halls. Postoperative care must be taken with application of elastic garments for a significant period according to the severity of the disease.
Conservative management
Manual lymphatic drainage, pump therapy, elastic garments, diet and exercises are used and strongly recommended during the rehabilitation period.
About Us
The Thessaloniki Lymphatic Center of Aristotle University of Thessaloniki is a designated “Network of Excellence” according to LE&RN, situates at Papageorgiou General Hospital. The lymphedema outpatient multidisciplinary clinic consults new patients in a weekly basis. The Thessaloniki Lymphatic Center provides conservative and surgical care and advocacy for patients with all kinds of lymphatic disorders (primary or secondary lymphedema and lymphatic anomalies). The center also focuses on research activities and education in health care providers.
Dr Dimitrios Dionysiou
Associate Professor in Plastic Surgery
Coordinator of Lymphedema Center
Dr Efterpi Demiri
Professor in Plastic Surgery
Chief of Plastic Surgery Department
Telephone: 14741 for an appointment at Papageorgiou Hospital – Lymphedema outpatient clinic
In android mobiles connect to the application: “Lymphedema App”